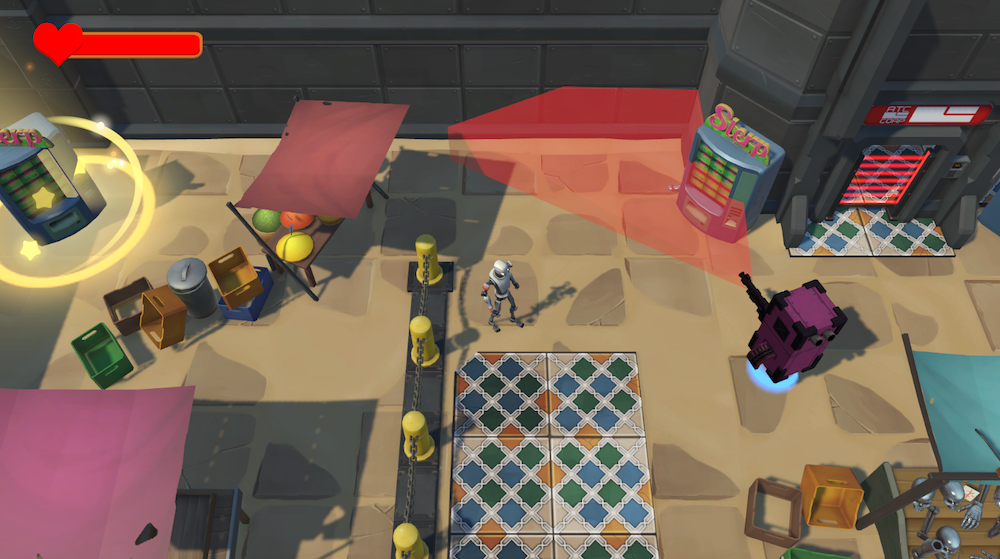
AI tools 4 Games
AI tools for games project
Supported by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation under grant PID2021-123368OB-I00
About AI tools 4 Games
The relationship between video games and AI research has not ceased to gain relevance in the last 20 years, since Laird and van Lent proposed video games as the "killer application" for the development of agents with human-like intelligence, becoming one of the main domains of experimentation for some modern AI techniques such as deep reinforcement learning. However, the adoption of these AI techniques in the professional production of video games is limited by the specific needs of the development of this type of systems.
The need to put AI techniques in the hands of the game designer, someone a priori without programming skills, connects with research in explainable AI or eXplainable AI (XAI). XAI has given rise to a great deal of activity in recent years, driven by the desirability of providing transparency to decision-making systems that increasingly affect more and more areas of our lives, especially due to the tremendous rise of intelligent systems based on deep learning. However, the aim of AITools4Games is not so much to explain to designers the decisions of AI algorithms, but to put in their hands tools that, supported by AI techniques, support the creation process, for which it is necessary for the designer to have not only a qualitative understanding of the model, but also to be able to modify it, to some extent. We seek, in short, to develop XAI techniques that enable the construction of intelligent and understandable authoring tools, where the creative process is reformulated as a collaboration between the designer and the system, in which both contribute to solving a problem.
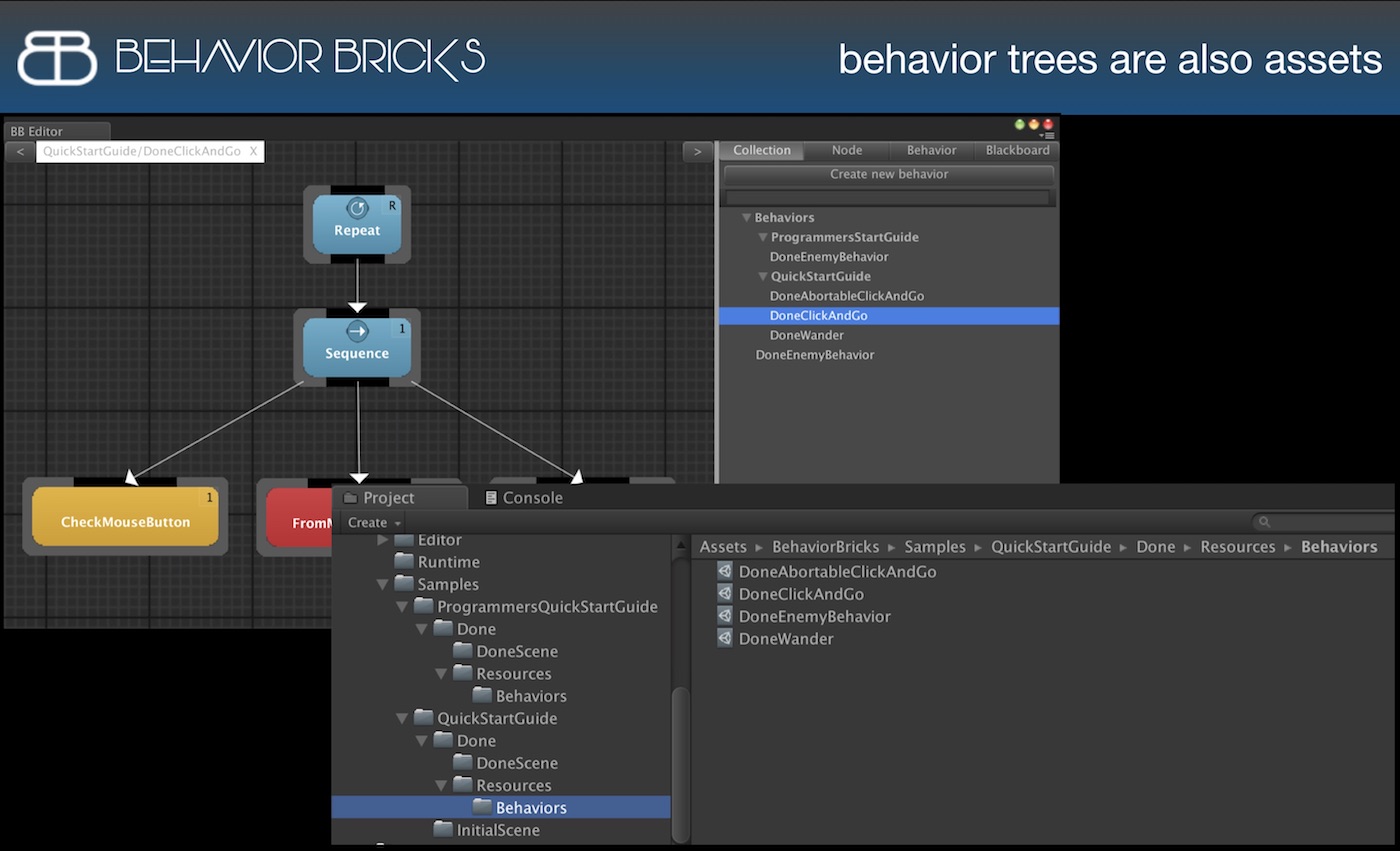
Based on our previous experience and its implementation in the video game industry, in AITools4Games we will deal with the development of learning by reinforcement, learning by imitation and planning techniques. In all cases we seek to advance the state of the art of the application of these techniques to the development of video games with features that allow their incorporation into tools for game designers. Although in each of the techniques we will have to explore specific solutions, there is a common denominator in all of them: to develop these techniques in such a way that it is possible to interleave the execution and modification of the models "in hot". A special feature of the models obtained in the application of AI to video games is the possibility of understanding their operation indirectly by observing them in action, i.e. playing the game. Our vision is that of a designer collaborating with the system in the creative process, running the model in its current state and being able to interrupt the execution when the behavior is not as desired, in order to refine the model, either by modifying parameters or by adding new training examples. The ability to interrupt and resume AI execution is common in video games, where it is more important that the rendering frequency of the scene is maintained than that the AI finds an optimal solution. At AITools4Games we propose to extend this ability of AI to be interrupted and resumed by bringing it into its own design process.
AI Tools 4 Games Software
AI tools 4 Games Publications
People in AI tools 4 Games

Pedro Antonio González Calero

Marco Antonio Gómez Martín

Pedro Pablo Gómez Martín

Antonio A. Sánchez Ruiz-Granados

Ismael Sagredo Olivenza

Pablo Gutiérrez Sánchez